Introduction to the Tutorial on the chlorine dioxide generator

Chlorine dioxide is used worldwide as a disinfectant and more important. This success is built:
- by the toxic effects on organisms,
- the high degree of independence from the pH of the water and
- the difference of the reaction by-products of chlorine dioxide to the reaction by-products of chlorine.
A detailed justification for the use of chlorine dioxide is in the newspaper article to Biological contamination of the filters and in Tutorial to Legionella to read.
The theme of the following lines is the on-site production (in situ) shown of chlorine dioxide in a generator.
Safety
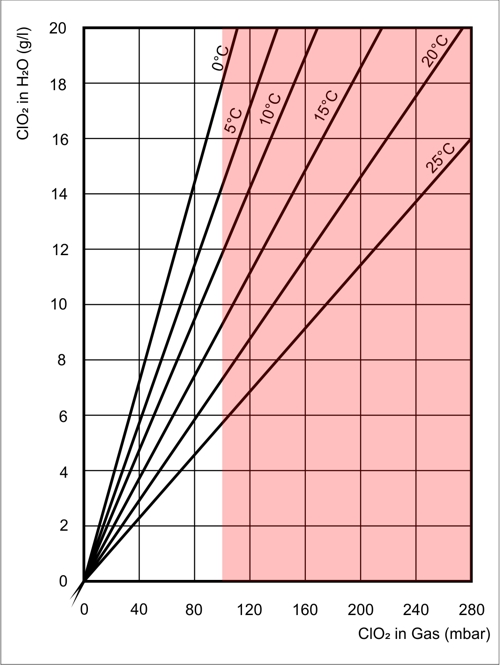
The concentration of chlorine dioxide in the water and the ambient temperature are decisive for the concentration of chlorine dioxide in air. At values greater than 10 volume percent is a risk of "spontaneous decay". Therefore, the concentration of chlorine dioxide in the water must be limited by the method and chemicals. Chlorine dioxide may not be transported. Therefore generators for the production on site usually the drug of choice.
Other safety conditions are formulated by the Association of German accident insurance.
The following document below from 1997 the essential rules are shown. The seemingly important points to distinguish from other plants with pure chlorine are marked in yellow.
 Loading...
Loading...
The document for download for registered users:
[wpdm_package id=’1440′]Right dosage and concentrations
Dosage in drinking water
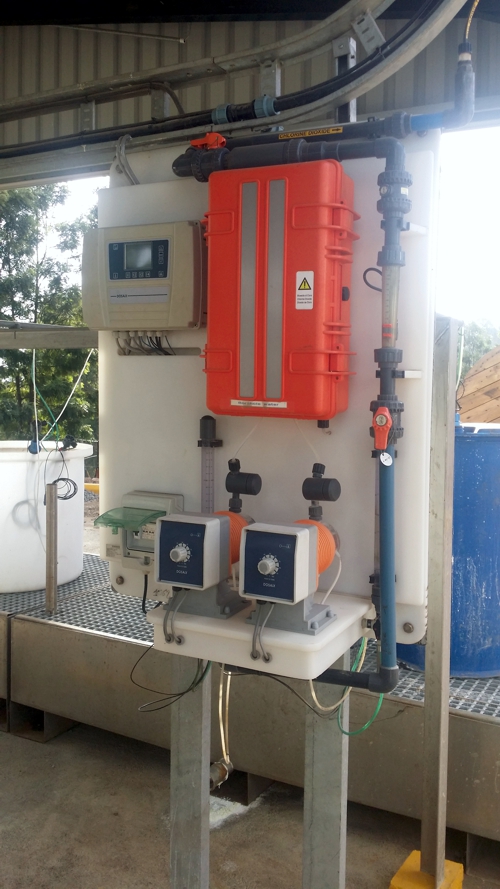

The disinfection of drinking water should be made only, if there is a need of responding to problems. Reasons for disinfection can be poor raw water quality, problems in the piping system or Microbiological contamination.
One of the permitted agent by drinking water regulations is chlorine dioxide. This Regulation specifies the following concentrations:
- At the point of dose maximum 0.4mg/l,
Closest to the first place of utilization a maximum of 0.2 mg/l
The farthest place of utilization is minimally 0.05mg/l.
Because there is a theoretical possibility, that the chlorine dioxide is converted to chlorates, in Germany only the "proportional metering" is possible. The volume flow of water and the flow rate of chlorine dioxide is adjusted proportional to the desired concentration.
The signal of the water volume flow is usually supplied by a water meter with output signal and the metering takes place via a suitable metering pump. This pump must be able to understand the signal of the water meter.
The consumption of chlorine dioxide is a dynamic process. Initially, a high consumption results in low concentrations at the donor sites so the concentration will rise after a few weeks.
If have been set at the metering point 0.4mg/l, it is therefore necessary, to examine the concentration at the first utilization point for compliance with the maximum value at regular intervals. To check a photometer should match DPD method Chlorine dioxide should used. It is advantageous, to monitor the measured values and the resultant actions. If the necessary actions are not known, the Tutorial calibration help. In the newspaper “Das Schwimmbad und sein Personal”, edition 10/2018, is the topic of calibration also edited and will soon be online.
It may be just as beneficial, the concentration of chlorine dioxide on a special sensor for chlorine dioxide DOSASens permanently measured and recorded.
Dosage in the process water

In the process-water principle, the rules apply as for drinking water. Nevertheless, it is, particular considerations of the process. The aim of the (disinfection) Measures should be formulated and fixes. Beneficial for the chlorine dioxide is here, that the tendency to form odor and taste change is much less than when chloride.
the target must be defined especially in the disinfection of water in open cooling circuits. In general, it is the goal, to prevent legionella in the aerosol of the cooling tower. Thus is important, that a minimum concentration of the disinfectant in the collecting basin is detectable.
Since operating conditions and ambient conditions change the proportional metering does not make sense. Instead, should a permanent measurement and control, for example, a good regulator be used.
For longer shutdowns of a cooling tower or a cooling circuit a permanent refresh mode should be scheduled, which prevents contamination during the decommissioning.
Dosage in filter flushing

is becoming more common to observe, that filters become contaminated. Because there increase the Legionella and other organisms in layers of activated carbon well and protected, must be regularly disinfected within the flushing. The applicable concentration is standing on the available time (contact time) dependent.
Here, no limits can be called. There remains only the possibility, to review the results of the measures. A detailed description can be found in Article on the topic Filterverkeimung, Published in: Das Schwimmbad und sein Personal, edition 09/2018.
Dimensioning of a chlorine dioxide generator
Fortunately, there are in the dimensioning of a chlorine dioxide generator a simple relationship of units: ppm = mg/l = g/m³.
Oxidation consumption

It is possible that minerals present in the water, which consume chlorine dioxide. In dimensioning this consumption must be considered. On the left the four major examples:
Of course, within cycle processes, the oxidation consumption is only to be considered once for filling and refilling. For open circuits such as the cooling tower entrained minerals from dust in the air have to be considered. Likewise, an advanced state of corrosion of metals in the system or an incomplete corrosion protection can significantly increase the oxidation consumption.

Photo Aquatic Center Saransk, Oxidation by oxygen in the air
Calculation process for volume flows
Calculation process for volume flows
The production capacity of a chlorine dioxide generator is given in grams per hour of chlorine dioxide. The volume flow of the water in m³/h multiplied by the maximum concentration in mg/l = g/m³, the capacity of the generator results in g/h. The following table shows the line of time with 1 (h) to leave.
Calculation process for volumes
Shall volumes, as the content of a water tank, are treated with chlorine dioxide, then missing the flow against time. The time must be calculated according to the requirements in the unit "hours". The volume of water in m³/h, divided by the time in hours multiplied by the maximum concentration in mg/l = g/m³, the power of the generator results in g/h.
In the following table the values in column F can be adapted to the local conditions and allow a rough dimensioning of the chlorine dioxide generator.
After registration, the table can be downloaded.
[wpdm_package id=’2270′]Consumption of the chlorine dioxide generator
For the production after the chlorite acid procedure becomes 9,0 percent hydrochloric acid HCl and 7,5 percent sodium chlorite NaClO2 and water and electric power consumed. The chlorine dioxide has a concentration of at the end 2 Grams chlorine dioxide per 1 liters of liquid.
The following table shows the green values in column F can be adapted to local conditions and provide an estimate of the consumption of chemicals and water. The representation of the electrical consumption is not included.
After registration, the table can be downloaded.
[wpdm_package id=’2293′]Operation of a chlorine dioxide generator
After generating the chlorine dioxide has to be dosed in an existing water system. The pressure of the water system must be overcome. If the energy and plant engineering effort should be kept low, then only the dosing pump works against the high pressure. The chemical reaction and its speed are independent of the pressure. Therefore, no special requirements for pressure resistance are necessary prior to dosing.
This generator type, additional dosing points can be easily supply. The production capacity of the generator can be distributed to a plurality of pumps. The dimensioning of the storage tanks, it is possible, to decouple the need of a shock dose and time-to-repair of production output.
This generator type, additional dosing points can be easily supply. The production capacity of the generator can be distributed to a plurality of pumps. The dimensioning of the storage tanks, it is possible, to decouple the need of a shock dose and time-to-repair of production output.
In the following presentation, the operation of such a generator is shown. Only mouse click in the area to start the presentation of a cycle. The presentation begins with the presentation of proportional sampling. The water meter outputs electrical signals to a dosing pump. The metering pump feeds the final chlorine dioxide in the water pipe.
After another click, the production of chlorine dioxide begins. Pay attention, the times for the chemical reaction are simulated in a few seconds.
One chlorine dioxide generator for multiple metering pumps
Often, the task is, dosing the chlorine dioxide at several points. In this case, it is possible, once to produce and consume several times. The performance of the chlorine dioxide generator must equal the sum of consumption. With this type of installation, the disinfectant can be targeted metered and general consumption can be reduced.
In the second very important aspect, the failure safety of the disinfection can be increased. Although chlorine dioxide is not indefinitely durable, you can continue to disinfect the time with a properly sized storage tank to an improbably necessary repair . The size of this tank can always be adapted to the requirements of the system.
In the following presentation, the operation of such a generator is shown. Only mouse click in the area to start the presentation of a cycle. The presentation begins with the animation of the proportional utilization by two pumps. The particular water meters send electric signals to a metering pump. The metering pump feeds the final chlorine dioxide in the water pipe. The chaotic series of pump corresponds to the expected reality.
After another click, the production of chlorine dioxide begins. Pay attention, the times for the chemical reaction are simulated in a few seconds.
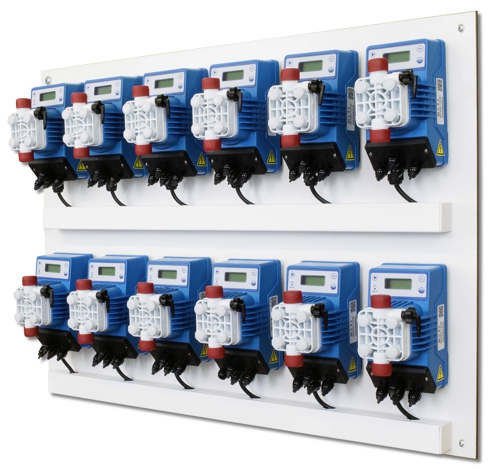

Redundant systems
Of course it is also possible, it is 50% to provide the power, each with a smaller chlorine dioxide generator. But this represents a financial investment. More important, it can be, to have the maintenance kit and important repair parts on site. Thus, the operation trained technician can perform the repair itself in the short term. Good manufacturers offer such training to the facilities at.
Wear occurs particularly through the use of aggressive chemicals at the seals and the diaphragms of the pumps.
Therefore generators, the chemicals in relation 1:1 to process, advantageous also in the use of spare parts. But it is to be observed, that the chemicals used require different sealing materials.
The following table shows the green values in column F can be adapted to local conditions and provide an estimate of the size of the storage tank for chlorine dioxide.
After registration, the table can be downloaded.
[wpdm_package id=’2295′]Chlorine dioxide generator with direct dosing
Another type of production works completely against the system pressure of the pipes. The chemicals and the water-brought together in the reactor under the same pressure. The reaction is caused by swirling of the components in the lower region of the reactor. The finished chlorine dioxide is metered from the upper part of the reactor into the pipeline.
This system can of course be converted to production in a memory. However, the dimensioning of the pumps must then take into account the lower pressure.
Chlorine dioxide generator without water dilution in the reactor

As described in the section "Safety" is there a relationship between the concentration of chlorine dioxide in the water and the risk of explosion. For this reason, in the rules of the DVGW, the concentration of chemicals used is on 9,0% for HCl and 7,5% limited for NaClO2. Do the chemicals in this concentration contact, without the water used for dilution , then there is a very low risk of explosion on contact with air.
For this generator type, a separate supply of water is installed and flow monitored. The path between the reactor and piping is designed to be extremely short. If necessary, a bypass is operated to the main line.
Chlorine dioxide generator with concentrated chemicals
As described in the section "Safety" is there a relationship between the concentration of chlorine dioxide in the water and the risk of explosion. In so-called concentrated chemicals, this danger is particularly. Therefore, attempts, with additional security- and monitoring capabilities to limit this risk.
The focus for the decision in favor of concentrated chemicals is the reduced transport costs. Water is usually available cheap. When balancing risks and benefits, the human factor should not be ignored. The level of education of local staff should be taken into account and adjusted as necessary.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.