Published in: Das Schwimmbad und sein Personal, edition 07/2020
… the third part on the pressure precoat filters.
| Preamble
The first article related to precoat filters in the edition 10/2019 was provocative and sparked some discussions. The second article, a location determination by Dipl.-Ing. Achim Rietz, has described the supposedly current status. Sometimes the current state glued also look at the past. But only together can the knowledge from the past and the present be used for the path to the future. And so has become one of the most famous specialists in the field of filtration, Dr. Pacik, reported in the editorial office and on a publication on test results for precoat filtration from the time of the so-called "yellow print" of DIN 19643 pointed out. We will come back later. |
To remember
Dipl.-Ing. Achim Rietz had in the magazine 05/2020 following comparison between pressure multilayer filter and pressure precoat filter with activated carbon filter (with identical graphics and diagram) drawn.
Graphic 1: Ratio of diameters 1 to 2,9 for 200m³ / h, Source: aqua&pools
A comparison of the space requirements of filter systems, the pressure multilayer filter and the pressure precoat filter with activated carbon filter is in Diagram 4 4 shown. For the pressure precoat filters, the diameters of the "Defender®" brand were used as before for the respective volume flow. In the additional stage with an activated carbon filter in the bypass of the filtrate water line, a partial volume flow of 20% scheduled.
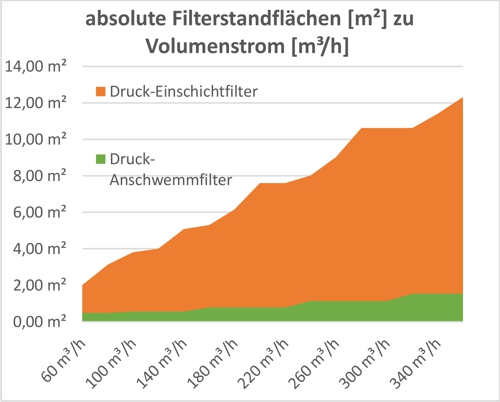
Diagram 2: Required stand space Pressure single-layer filter and pressure precoat filter
The comparison limps a little!
... because the majority of experts see the comparison in this way:
- Single layer filter = sand and
- Multi-layer filter = activated carbon = adsorption.
This is only the half truth. In DIN 19643-2:2012-12 point 4.4.2 there is no layer of activated carbon in any table when building up layers.
So let's get some order in the mess.
Probably in the DIN 19643 Brown coal coke (so-called H material) and known its problems., but a desired adsorptive effect is not described.
Source sbf-online.com: “The filter bed of multi-layer filters consists of several filter materials of different densities and grain sizes. The filter materials are matched to one another, that after the filter rinsing the layers are separated and first the coarse filter material in the direction of filtration (for example filter anthracite) is flowed through. "
In table 3 of DIN 19643-2:2012-12 then follow layer structure under the condition of powder-activated carbon dosing in multi-layer filter.
That is why the multi-layer filter is not yet equipped with adsorption per se. This only happens through the targeted selection of a suitable filter material according to the point 4.5.2 Adsorption through multi-layer filtration: “If the filter is equipped as a multi-layer filter, so disinfection by-products can be eliminated by using suitable filter material with adsorption capacity."
... and not every disinfection by-product is adsorbed by every activated carbon!
Even if the scholars argue about the names, 120/5000 so is regardless of the direction towards the adsorption ability, the opinion about a certain order has become common:
- Activated carbon, A-coal, on different bases, with the highest adsorption capacity,
- Filter coal N based on hard coal with medium, Adsorption capacity and
- Filter coal H based on brown coal coke with low adsorption capacity.
The manufacturers do not even agree on the name, for example, the CSC filter carbon H 500+ of the supplier Hydrotechnik advertised as coal-based.
I would like to quote the source sbf-online.com again: „Adsorptionsfähigkeit: Sand and anthracite N are inert, so without any adsorption ability. Filter carbon H has an inner surface of approx. 320 m2/g a modest adsorption effect, which is quite sufficient under normal circumstances, to so-called bound chlorine, but not THM, to reduce sufficiently. Have activated carbons with 900-1000 m2/g usually the approx. triple adsorption capacity compared to filter carbon H and effortlessly remove bound chlorine inclusive. THM “
A measure of the adsorption capacity is the already mentioned inner surface in square meters per gram. Another measure is that (measurable) Iodine number in milligrams per gram. With this number can be used to analyze, whether the filter layer is already loaded.
Adsorption ability vs. Germination risk
High adsorption ability is not limited to the by-products of chlorination, but also on the chlorine itself!
Thus, with a high adsorption ability, there is also a maximum risk of contamination. Is a maximum effective layer of activated carbon flowed through, so all of the free chlorine is unwantedly adsorbed in the first few centimeters.
All other areas are then chlorine-free and the biofilm can spread freely on the huge surface.
Not least because of this, the authors of DIN wrote 19643 in the point 4.5.2 "Because of the increased risk of contamination, the use of activated carbon should be avoided."
For the sake of completeness, I now also have an incomprehensible addition on the same point:
This risk is lower with brown coal coke, which is why this should be given preference. "
.
The relationship between adsorption capacity and risk of contamination is the same. As long as the brown coal coke is adsorbed there is also a risk of contamination! You can choose: Either red eyes or germs.
Photo 01: Source Fotolia 195652332
First result:
Either you compare both sides, the multi-layer filter and the pressure precoat filter, without any adsorption or one compares both sides with the adsorption in an external activated carbon container. The positive rating shifts slightly towards the pressure precoat filter.
Adsorption on powdered activated carbon, where's the difference?
Let's take a look first at DIN 19643-2:2012-12 point 4.5.3.1: “Powdered activated carbon must be dosed proportionally to the volume flow of the processing plant. The powder can be dosed directly into wetting devices and pumped into the volume flow of the system or prepared as an activated carbon-water suspension and dosed as such. "
The powder is dosed into the volume flow, gets the opportunity, to adsorb in motion, and remains on the surface of the filter layer. The main difference: The loaded and possibly contaminated powdered activated carbon is removed together with the germs every time the filter is rinsed!
The powdered activated carbon simply doesn't get time, to support the germs, because the dosage is adjustable to the need for the chlorination by-products. You just have to adhere to the requirements of DIN 19643 hold for filter cleaning.
Contamination, the other extreme!
Imagine yourself, a pool master has a multi-layer filter with slowly increasing differential pressure. And because he wants to save water, he activates the air purge for a few seconds every day. This whirls the dirt and the filter layers thoroughly together and lowers the differential pressure back to a good value. If he does it every day, then this technican can operate his filter for several weeks without using water. The germs grow unhindered and can spread. Inconceivably?
No, reality! But on pressure precoat filters.
In the pressure precoat filter has a thin layer of filter aid and dirt on the fabric. This layer must be removed from the tissue for regular cleaning, so to speak "dropped", become. At least one manufacturer supports this "dropping" with a device.
Normally, the discarded mixture of water and filter aid and pollution is drained into the sewage system. The DIN 19643 point 4.4.3.4 call it that: "The filter material is basically discarded in the course of filter rinsing with the rinsing waste water."
The differential pressure also drops, if you simply washed up the thrown mixture again. Soiling and germs are not removed, but may also circulate in the clean filtrate area. This saves water, Filter material and even sewage costs.
The provider of the device is not to be blamed for the use and every pool master is under cost pressure. But then you could omit the filter entirely.
There are pressure- precoat filters alternatives without this device and its cost, which only use the filter according to DIN 19643 allow!
The possible non-adsorbing materials
A number of filter materials are now known for precoat filters and are used. The risk potential, that comes from the dusts of these materials, we already had in part 1 in newspaper 10/2019 compared. Although a rather one-sided rumor has been spread in the past, it’s about the same for all materials. Important point: Respiratory protection must be used.
Precoating with adsorption layer
The question naturally arises from the previous thoughts at some point, why precoat filter technology does not work with multiple layers of different materials.
It is not so easy, because factors have to be coordinated.
- At what water speed does the selected filter auxiliary substance accumulate?
- At what water speed can the selected filter auxiliary substance not settle in the filtrate area during the circulation?
- At what water speed does the filter auxiliary substance densify too much?
- What porosity does an adsorbent layer need?, so that there is a small pressure difference?
- What layer thickness must an adsorbing layer have?, to give the reaction enough time?
- What iodine number should the adsorbent layer have?, to achieve the desired effect?
- At what water speed can the adsorbing layer be precoated?
- How must the adsorbent layer be protected from physical contamination, to maintain chemical reactivity?
Answers from Dr. Daniel Pacik
In the past decades, precoat filter technology in Germany has been dominated by vacuum precoat filters. For this reason, the investigations primarily related to vacuum precoat filters, but with the same target: to integrate an adsorption stage.
Dr. Pacik is even then come to a positive result. With the kind permission of Dr. Pacik are partially reproduced here passages of the original text.
The full version of the scientific article can be called up using the QR code.

Dr. Pacik does not only give a good reason for the need for an adsorption stage, but also a additional solution:
Several filtration systems are used in public pool construction, which can generally be operated with downstream chlorination. Beside the bed- (Single layer- respectively. Multilayer) filters it is about systems, known as "precoat filters". The following explanations are intended to give the professional world an interesting variant of that after the vacuum- or approach the precoat filtering that works using the vacuum principle.
It is known, that in disinfecting of swimming- and pool water made from chlorine and organic substances (carbon- and nitrogen compounds) unwanted reaction products can arise. These pollutants can get into the pool water through the fill water as well as through the swimmer. The reaction products, that arise from chlorine and organic contaminants, are primarily trihalomethanes, AOX and chloramines (bound chlorine).
If the concentration in the pool water is too high, these substances and groups of substances can impair human health. For example, the trihalomethanes are suspected of having carcinogenic and mutagenic properties. The draft of the swimming pool water ordinance and the available yellow print of DIN 19643 (Treatment and disinfection of swimming- and pool water) therefore include guidelines for chloramine (0,2mg/l) as well as for trihalomethane (20µg/l). It is essential to pay attention to this, to fall below the specified guide values as far as possible according to the minimization requirement.
Extensive studies by the Federal Health Office have shown in this connection, that by using special powdered activated carbon trihalomethanes and chloramines can be reduced far below the recommended values.
Since these experiments initially only with the combination of flocculation – Filtration chlorination were carried out, it was interesting to learn, whether another type of filtration – vacuum precoat filtering – can achieve similarly good results.
Aim of further, with the tests carried out on the precoat filter it was therefore to be checked, whether the powdered activated carbon developed for fixed bed filters can be adapted to the process combination of precoat filtering and chlorination. It should also be noted, which modifications of the activated carbon are suitable for the practice of precoat. In this context, it is PACIK's dissertation (1986) to call, in which reference was made to the further development of the precoat with diatomaceous earth and activated carbon.
The statements of the yellow print of the DIN 19643 (May 1993) – Digit 10.2.2 and 13.3.2 (Part 1) as well as digits 3.5.2.1 respectively. 3.5.2.2 (Part 2) on the other hand, the problems mentioned are very poor and therefore cannot be used in practice to implement the knowledge gained.
... because the test of the process with the structure of the filter layers on the personal resilience, the so-called b-value from DIN 19643: 1976 section 18 "Determination of the personal burden for not in section 7 Process combinations mentioned“ was not included.
The DIN 19643 has been the state of the art for years. In particular, it clearly describes the parameters of pool water quality and thus the mandatory requirements, the pool water treatment systems must meet. With the help of the rules for determining the personal burden, of the b value, it was possible for all interested parties, to develop new treatment methods, to have them checked and to obtain a reliable assessment basis for your systems via the b-value. This will get everyone involved, Client, guests and manufacturers, the certainty and security, that the processing plant tested in this way corresponds to the state of the art.
b value
Who the old DIN 19643 now not at hand, here is a simple explanation of the b-value:
The b-value indicates, the amount of oxidizable substances that the filter system can remove from the water. The amount of oxidizable substances is examined via the equivalent of the “potassium permanganate consumption”.
Under operating conditions, regularly over at least 6 Hours, the oxidizability of the water was measured before and after the filter. Both values, before and after, make a difference. The maximum is determined from the large number of these differences.
This maximum is divided by the contamination, that brings a single person into the water as the default.
In this way, the processes were comparable and the developer could register them for inclusion in the DIN.
That the so-called “b-value way”, the yellow print of DIN 19643 (May version 1993) completely disregarded, correct is, shows success. In the past, a successful b-value determination was carried out 7 times, like in the newspaper "Archiv des Badewesens" 3/80 and 5/81 is described. In the past, this meant security and protection for the manufacturer 7 times. No manufacturer can reasonably do without this security and protection based on the state of the art.
These principles still apply to vacuum precoat filtering with subsequent chlorination. Such sophisticated precoat filter technology is not only used in pool water treatment, but is widely used in other areas of liquid filtration. Application examples can be found in the filtration of beverages such as beer, Lemonades, in the separation and separation of oils, the filtration of technical liquids, the filtration of fruit juices, Circulating water, Condensate treatment, Elimination of the finest impurities by adsorption from nuclear reactor water, Drink- and bath water treatment.
This broad application technology results naturally, that certain criteria have to be assumed for each of these diverse tasks, to succeed.
The filter auxiliary substances and their correct selection in purity quality, Fineness, Permeability, Adsorption capacity and many other specific properties determine success in the first place. A look at the filter aids available today makes this variety of choices clear:
Asbestos flocks, Perlite, floccible ion exchangers, inerte flockbare Polyacryle, Diatomeenerde, Diatomaceous earth, Potato starch, powderable activated carbon, Cellulose and more.
All of these filter additives are available in many qualities and grades. There are also promising attempts to develop new filter auxiliary substances, especially for water treatment.
The overview makes it clear, that the precoat filter technique in its application, even when swimming- and pool water, needs to be carefully considered and tested.
Another, decisive factor in precoat filtration in general is the filtering speed. The task decides on this filter speed. For example, if only mechanical cleaning filtration is desired, is usually up to relatively high speeds 8,0 m/h, in exceptional cases up to 10,0 m/h, reachable. As a rule, a filter auxiliary substance in a specified manner is sufficient for mechanical filtration, proven quality.
However, adsorption is also required in addition to the mechanical precoat filtering, as a rule, the filter speed must be greatly reduced, in special cases up to 1,5 m/h, because the adsorption intensity of real dissolved ingredients in a liquid depends on the contact time (of the filter speed) dependent. To solve this filter- and adsorption task it is advisable, considerations about a special, combined design of a multi-layer filter cake, to achieve the desired success.
Because the cleaning of- pool water with the help of precoat filter technology can only be achieved by combining filtering and adsorption, must be paid attentionto the structure of the filter cake and the selection of the appropriate filter speed in experiments.
Instructions for the technical management of precoat filtration is provided by DIN 19624 again. This DIN gives an exact description of all parameters, a technical precoat filter design must take into account.
The DIN 19624 however cannot describe, which filter auxiliary substances in which combination at which filter speed can solve the task, for example. swimming- and pool water according to DIN 19643 prepare accordingly. This can only be done through experiments, Examinations and reports, including b-value reports, be found out and confirmed.
Consequently, it says in the DIN 19624 under.
- Terms
3.1. In precoat filters, filter auxiliary substances and suitable additives are uniform as a result of the water flow, porous filter layer precoated up on the surfaces of filter elements.
3.2. As filter auxiliary substances powdery or fibrous are used, surface-active substances used, mainly for the removal of undissolved constituents of the water.
3.3. Additional additives can be used in combination with filter auxiliary substances. Your preferred tasks are preparation goals, the about filtration by section 3.2 go out.
In the following points 3.4, 3.5 and 3.6 she speaks generally of filter auxiliary substances, Basic precoating, Additional precoat and filter elements.
But you have to get the impression, that the DIN 19624 was misinterpreted as a recipe book and parameters were read out and applied indiscriminately and without serious tests, just like that was created before the DIN 19624 obviously happened.
This is the only way to explain it, that ALTHAUS and PACIK had to find unsuitability during a series examination on precoat filters of various types. This was followed by attempts to use other filter auxiliary substances due to the negative consequences for precoat filtration, for example. Activated carbon, and attempts to build effective layers.
To date, however, only one method has been known and described in the literature, with success the proper b-value- Examination according to KOK guidelines and DIN 19643 has passed. With Dtr. TGB. – No. A 1955/79 from 4.12.1979 this scientific b-value report for precoat filtration from ALTHAUS and PACIK, formerly Hygiene Institute Gelsenkirchen, developed.
The filter technology tested with the above-mentioned report is based on the technical implementation of anchored experience in the literature. The DIN 19624 served as the basis for the selection of the parameters. The procedure described by the expert
Diatomaceous earth-activated carbon-vacuum wash filtering-chlorination
is the current state of the precoat filter technology and is therefore the basis of DIN 19643 to rate.
Dr. Pacik also describes a 3-layer structure with the following properties:
Layer I:
To protect the filter from greasy deposits and as the basis for an effective layer build-up of the entire filter cake, a first layer is precoated up to form a deposit.
Layer II:
On this layer (I) the activated carbon layer is built up in a further process (II). This second layer can be varied. The reason lies in the different nature of the fill water available. The maximum amount of activated carbon to be washed 200 g/m2 Filter surface
Layer III:
To protect this activated carbon layer, the filter layer becomes diatomite (III) precoated ashore; this completes the basic precoating.
The internal filter circuit then switches to the external circuit (Pure water inflow system of the swimming pool) switched.
The incoming, polluted pool water (Row-Water) filter auxiliary substances are constantly added via a special secondary dosing system.
From the beginning to the end of the pool water filtration that is now possible, the incoming pool water (Row-Water) continuously added diatomite as an additional precoat. The growing pre-filter layer is thus formed.
With the addition of chlorine and stabilization of the pH – runs the value in this form, successfully at a filter speed of up to 5m/h, state-of-the-art treatment of swimming- and pool water in the process combination
Diatomaceous earth-activated carbon-vacuum wash filtering-chlorination.
It is important here, that during the entire precoating process associated with the filtration, the layer structure is not destroyed and the metering of diatomaceous earth is not interrupted during the secondary precoating.
The filter principle works in the following way:
In the incoming pool water, specific, undissolved particles of diatomite (Diatomaceous earth) envelops, respectively. deposited simultaneously with diatomite on the growing prefilter layer. This layer remains porous due to the permanent additional build-up. A thorough mechanical filtering of all undissolved ingredients takes place in the filter layer. The pool water meets in such a purified form, in principle loaded with only dissolved ingredients, on the activated carbon layer. This is where diffusion and adsorption take place as well as degradation processes of the really dissolved ingredients promoted by activated carbon; including the trihalomethanes and chloramines.
A clogging of the pores of the inner surface of the activated carbon is not possible due to good pre-filtration through the filter layers.
Destruction of the filter cake described ends the effectiveness of the filtration. A reprecoating of the conglomerate resulting from rinsing or blasting must be expressly excluded.
Now in the pressure precoat filtration
A few years have passed since scientific work. The technologies have changed, but also the market.
The vacuum precoat filter in the swimming pool industry also made things quite easy: Open up, Filter auxiliary substances (Diatomaceous earth) fill in, wait up until everything is precoated. Modern computers dictate a time, one could also measure the turbidity. Supposedly you only had to wear a protective mask against the dust.
At least one manufacturer of pressure precoat filter technology has refined this principle and sucks the filter aid material over the fabric into the empty raw water area of the filter. The fine dust in the exhaust air finds its way ...
The empty raw water chamber
In the aforementioned method, the condition of the empty raw water chamber prevents the layered structure of the filter cake as suggested by Pacik for the vacuum precoat filter.
The secondary precoat
... has probably been forgotten in swimming pool technology. As a rule, it is onetimes precoated ashore and serviced, until the differential pressure has reached its limit. On the other hand, you can extend the useful life of a filter cake with the secondary precoat. However, at least one can build up a layer of the filter additives.
The advantages of pressure precoat filters
… have therefore not reduced. Here we have only compared apples with apples and adsorption level with adsorption level.
Additional benefits, that can arise from the layer structure of the filter additives, have been known since Pacik's scientific work. The details of the materials are contained in the original and can be viewed using the previously printed QR code.
| Conclusion:
A repetition, but still: It is always recommended, first the big picture (the procedure) to look at and then change a detail after. It is similar with filter refurbishment. In the newspaper 04/2020 we looked at the mechanical renovation of fiberglas filters, here it is now the thought “When is it worth changing to a different filter system??“ But also, if only the filters are considered, is it worth, to get advice. Via the website www.aquaandpools.de everyone can get in touch or get rid of clues. Dr. Pacik, thank you for support and advice. aqua&pools |

 Loading...
Loading...

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.